
Air travel is growing, but it also increases carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. This makes the need for cleaner fuels more urgent. Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a promising solution. It can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 99% compared to regular jet fuel. SAF is crucial in the aviation industry’s move toward net-zero carbon emissions. In this post, we’ll explain what SAF is, how it compares to traditional jet fuel, and what the future might hold for it.
What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)?
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a type of fuel made from renewable resources, such as waste oils and algae. Unlike regular jet fuel, which comes from petroleum, SAF is designed to be much cleaner. It can cut lifecycle CO2 emissions by up to 99%. The best part? SAF can be used in existing aircraft without any changes to the engines or fuel systems. This makes it a practical choice for airlines looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
The Current Status of SAF
SAF Production and Usage
Right now, the production of SAF is still small. In the United States, only about 4.5 million gallons are produced each year. That’s not nearly enough to meet the needs of the aviation industry. However, some airlines are starting to use SAF in small amounts. They see it as an important step toward achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
The biggest reason airlines are interested in SAF is because it can reduce CO2 emissions significantly. But, the higher cost of SAF compared to regular jet fuel is a major hurdle.
Environmental Benefits of SAF
SAF is much better for the environment than traditional jet fuel. By using renewable resources, SAF can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 99%. It also helps lower other pollutants that affect air quality around airports. This makes SAF a key part of the aviation industry’s plan to reach net-zero carbon emissions.
Economic Considerations
While SAF is great for the environment, it’s currently more expensive than traditional jet fuel. SAF can cost up to 700% more than regular jet fuel. This high cost is due to the small scale of current production and the advanced technology needed to make it. However, efforts are being made to increase production and bring down costs. For example, the U.S. government has launched the “SAF Grand Challenge” to boost production to 3 billion gallons per year by 2030.
How SAF Compares to Traditional Jet Fuel
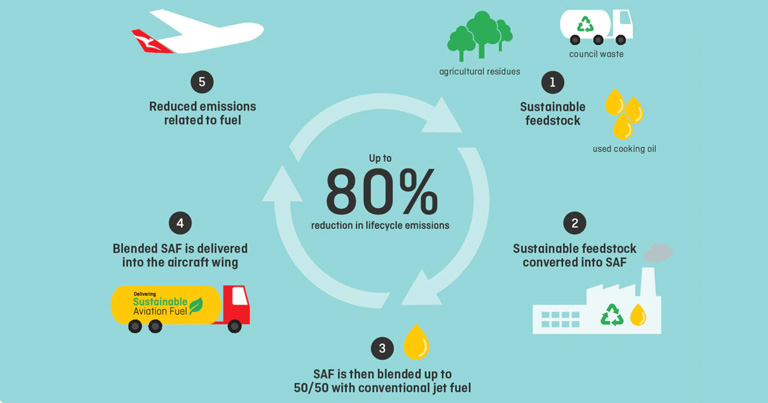
SAF is very different from traditional jet fuel. Traditional jet fuel comes from petroleum, which releases a lot of CO2 when burned. SAF, on the other hand, is made from renewable resources that absorb CO2 during their growth. This helps offset the emissions produced when the fuel is burned.
In terms of performance, SAF works just as well as regular jet fuel. It meets all safety and efficiency standards, and it can be used in existing aircraft without any modifications. However, the higher cost of SAF is a major challenge that needs to be addressed.
Challenges Facing SAF
Despite its benefits, SAF faces several challenges.
Limited Production Capacity
The current production of SAF is far below what is needed to meet global demand. Increasing production will require significant investment in new facilities and technology.
Higher Production Costs
SAF is more expensive to produce than regular jet fuel. This high cost is a major barrier to its adoption. To overcome this, the industry needs to find ways to make SAF cheaper.
Need for New Infrastructure
While SAF can be used in existing aircraft, its widespread use will require new infrastructure. This includes building more production facilities and creating supply chains to transport SAF from these facilities to airports.
Potential Competition with Food Production
Some SAF feedstocks, like certain crops, might compete with food production. This raises concerns about the sustainability of using these resources for fuel. The industry is exploring alternatives, such as algae, that do not compete with food production.
Regulatory Challenges
There are also regulatory challenges. Different countries have different rules for SAF production and use, making it difficult to adopt SAF on a large scale. Establishing global standards will be crucial for the widespread use of SAF.
The Future of SAF

Despite these challenges, the future of SAF looks promising. Here’s why:
Increasing Production Capacity
Efforts are being made to significantly increase SAF production. The U.S. “SAF Grand Challenge” aims to produce 3 billion gallons per year by 2030. This will require a lot of new facilities and investment.
Technological Advancements
Researchers are working on new technologies to make SAF production cheaper and more efficient. This includes exploring new types of SAF, like synthetic fuels, which could be even cleaner than current options.
Regulatory Support
Governments are starting to provide more support for SAF. This includes offering incentives for SAF production and requiring airlines to use more SAF in their fuel mix. For example, the European Union has set a target for airlines to use a minimum percentage of SAF by 2030.
Global Collaboration
The aviation industry is working together to solve the challenges facing SAF. Airlines, fuel producers, and governments are sharing knowledge and resources to increase SAF production and adoption.
Economic Viability
As technology improves and production increases, SAF is expected to become more affordable. This will make it a more attractive option for airlines, especially as the cost of carbon emissions continues to rise.
Conclusion
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is a key part of reducing the aviation industry’s environmental impact. It can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 99% and help the industry achieve net-zero carbon emissions. However, challenges remain, including high costs and limited production. Overcoming these challenges will require investment, technological advancements, and global collaboration.
To support this transition, you can choose airlines that are leading the way in SAF adoption. By doing so, you help encourage the use of cleaner fuels and contribute to a more sustainable future for aviation.